A Global Tooling Manufacturer Goes 3D
Wilson Tooling International turns to Carbon’s DLS technology to reimagine a critical part.
Anyone who attended Fabtech this year likely found it hard to miss the noticeably expanded 3D/Additive Manufacturing Pavilion, with dozens of companies inhabiting a giant swath of real estate situated between the finishing and forming/fabricating sections of the B hall.
It made sense that Wilson Tool International, the planet’s largest independent manufacturer of tooling systems and accessories, wasn’t located in the additive manufacturing pavilion. But with Wilson Tool’s recently launched 3D printing division—Wilson Tool Additive—generating the highest level of foot traffic in the company’s booth this year (at least during my two visits over the course of two days), it will be interesting to see where the company resides at Fabtech 2019.
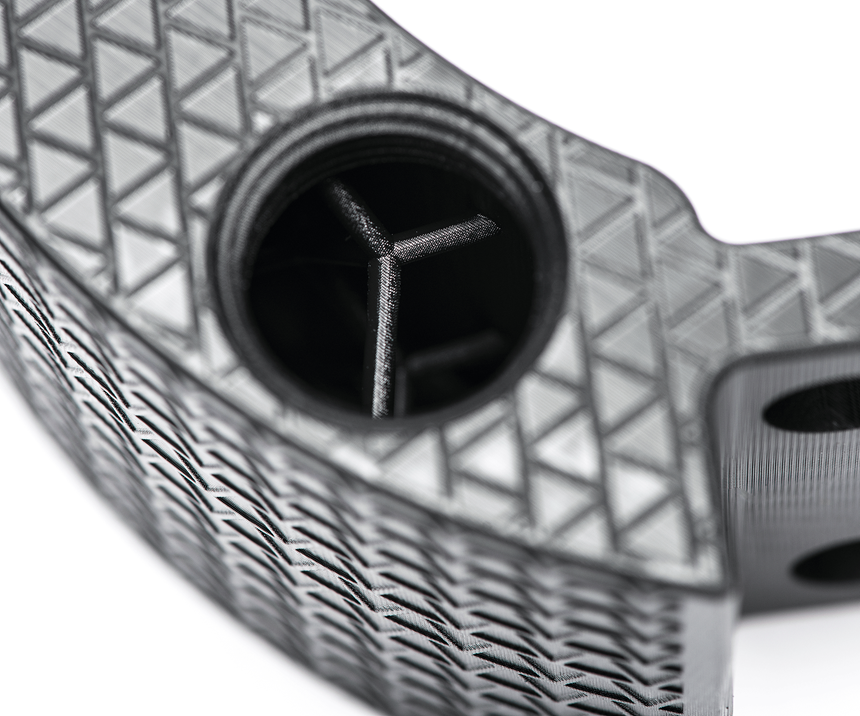
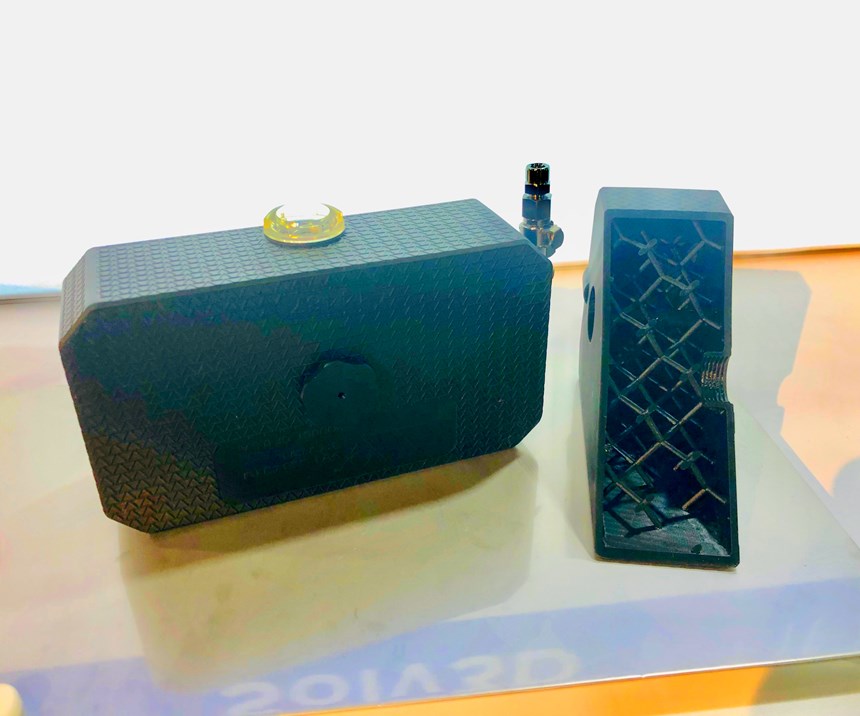
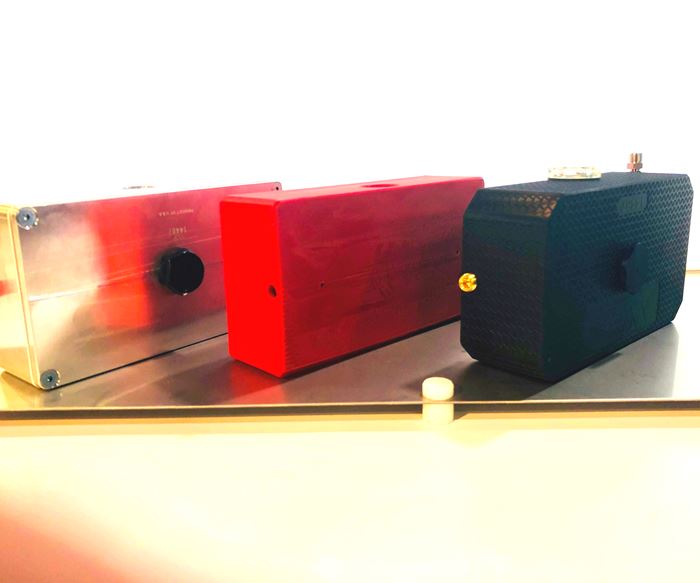
The spotlight at Wilson Tool’s booth this year was the company’s QuickTap tapping tool oil reservoir—essentially a small rectangular box which, without insight into its backstory, may look unexceptional. But, as Wilson Tool’s senior additive manufacturing engineer Bryan Rogers told me at the booth, the now-3D-printed reservoir represents a giant leap in the company’s production capabilities for this deceptively intricate device.
These oil reservoirs are a high-demand item due to the popularity of Wilson Tool International’s QuickTap tapping tools for punch presses. The manufacturing process for the reservoirs traditionally involved fabricated cold-rolled steel that was punched and formed into seven, eight or nine components, depending on which of the six available configurations of the reservoir was being manufactured. Because these seven (or eight or nine) components were then welded together, each tank was subjected to a lengthy testing process to ensure the seals did not leak when subjected to pressurization. All of this increased the lead time for the reservoirs and meant that Wilson Tool needed to maintain high inventory levels to ensure timely delivery. Of course, each of these factors drove up per-part costs.
After attempting to find a better solution, including blow molding as well as a machined reservoir manufactured from aircraft-grade aluminum, Wilson Tool International turned to 3D printing—specifically, to Carbon’s Continous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) technology for Digital Light Synthesis (DLS).
Rogers told me that Wilson Tool International has been using 3D printing since 1996 and began prototyping functional parts in 2012. But after working with Carbon to create a proof-of-concept part that was able to hold oil, interface with tubing and provide impact absorption, the two companies settled on manufacturing the oil reservoir with 3D printing. They selected Carbon’s rigid polyurethane material, RPU 70, for the part and qualified the part across multiple criteria. The result is a reservoir that is produced as a single part and therefore at a much lower risk for leakage and failure. The 3D-printed part is up to 60 percent less expensive and has a lead time up to 50 percent faster than the traditional part. The digitization of the part means there is no need to warehouse a large inventory of the reservoirs, which eliminates the cost of storage and means that new iterations of the part can be achieved quickly.
With enough success, who knows. Maybe at Fabtech 2019 you’ll find Wilson Tool International among its new peers in the Additive Manufacturing Pavilion.
Read Next
AM 101: Digital Light Synthesis (DLS)
Digital Light Synthesis (DLS) is the name for Carbon's resin-based 3D printing process. How it works and how it differs from stereolithography.
Read More4 Ways the Education and Training Challenge Is Different for Additive Manufacturing
The advance of additive manufacturing means we need more professionals educated in AM technology.
Read MoreAt General Atomics, Do Unmanned Aerial Systems Reveal the Future of Aircraft Manufacturing?
The maker of the Predator and SkyGuardian remote aircraft can implement additive manufacturing more rapidly and widely than the makers of other types of planes. The role of 3D printing in current and future UAS components hints at how far AM can go to save cost and time in aircraft production and design.
Read More