Jason Szolomayer has a major five-year plan. Founder of the nonprofit 3DP4ME, he intends to provide hearing aids for thousands of individuals in underserved communities in the Middle East. The devices will be custom-made for each patient — made possible through a combination of specialized scanning and 3D printing. But in some ways the technology is the easy part; the challenges the nonprofit still needs to clear are more in the realm of design, workforce, training and funding. Overcoming them will not only allow for ongoing production of custom assistive devices, but also improve overall healthcare in the region, focused on Jordan and Syria.
“How do you decentralize care?” Szolomayer asks. It’s an important question, because what 3DP4ME is setting out to do is not just produce hearing aids in the Middle East, but help the region’s audiologists treat more patients. Ultimately, it is not just about making these devices but getting hearing aids to more people who need them, by implementing a workflow that is more digital and automated.
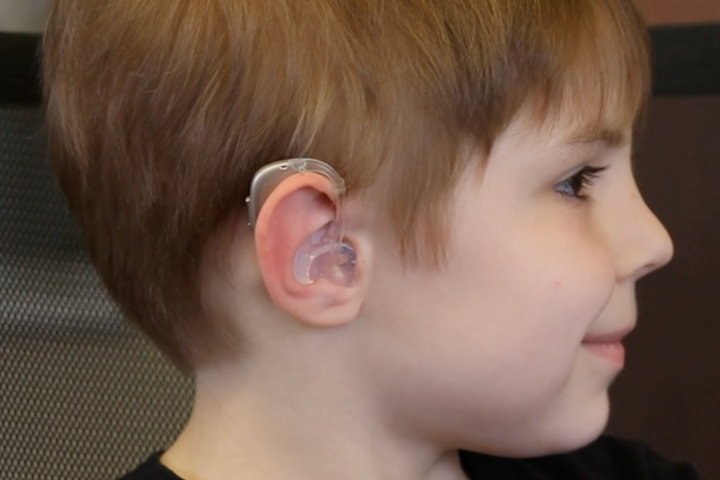
The earmold is the clear portion of the hearing aid seen here that fits inside and must be customized to the shape of the wearer’s ear. Photo Credit: Microsonic Inc.
Custom-Fit Hearing Aids for Children
Hearing aids come in two basic models. There are dome-style hearing aids that sit inside the ear canal and are not necessarily visible from the outside; these hearing aids are generally standardized, and are mostly used by adults. Then there are the hearing aids most commonly used by children: These have an external piece worn behind the ear, and a custom “earmold” that fits snugly in the ear canal (similar to some styles of earbuds). The custom pieces are made specific to each patient from acrylic or silicone, and this is the portion of the hearing aid that 3DP4ME 3D prints, alleviating the challenges and steps involved in manually producing them.
The organization recently secured a grant from Intel and Accenture to fund a project called the Hearing Express, the pilot of which is underway as of November 2022. Through this pilot, 3DP4ME will identify 50 children in need of hearing aids and provide them with care, including custom earmolds to be made at its recently-established production facility.
The production site is equipped with an Asiga Max digital light processing (DLP) printer for earmold production, along with cleaning capacity. A curing system and tumbler will be added for finishing the earmolds.
3DP4ME also owns a specialized scanner for capturing ear anatomy. Made by Lantos Technologies, the scanning instrument inflates inside the patient's ear like a balloon, capturing tens of thousands of data points in a matter of seconds. These data points can be converted into a 3D printable design for the needed earmolds. (The device, though, does not yet work for small children — for them, the best course of action is to take a physical ear mold impression and scan that to create the STL file.)
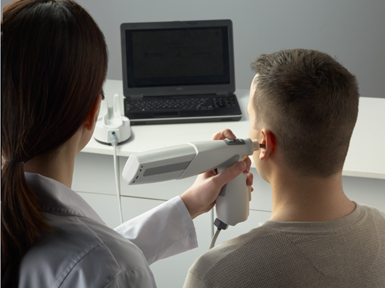
The Lantos scanner captures three-dimensional information about the patient’s ear anatomy; that data can be used to design the custom, 3D printable earmold. Photo Credit: 3DP4ME
Together, 3D scanning and 3D printing eliminate hours of time needed to produce patient models and to form and fit custom earmolds using conventional methods. And, while the 3D printer will not travel, the scanner can be entirely mobile — providing a way to bring care to patients wherever they are.
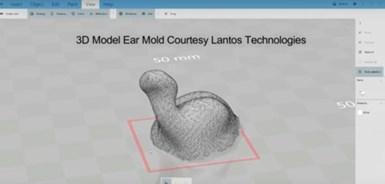
An STL file for an ear mold based on scan data from a Lantos Technologies scanner. Photo Credit: 3DP4ME
Remaining Challenges
Soon all the physical components will be in place to produce these devices, which leaves the trickier expertise and digital aspects of the process. “Technology transfer with CAD is one of our challenges,” Szolomayer says. Designers need training to understand how to work with an ear scan and ensure that the ultimate earmold design will print correctly. And while working digitally speeds up the workflow for producing the earmolds, each new scan still requires some amount of human processing and expertise. “A designer might spend 10 to 12 minutes per file,” he says. “We're exploring AI solutions that could get that down to just a few minutes for faster turnaround.”
Personnel is also a challenge on the front end of the workflow, due to an overall lack of audiologists in certain parts of the world. While these specialists exist in Jordan, they are rare, and each one can see only a few hundred patients per year. In some countries like Algeria there are none of these healthcare providers at all, Szolomayer says. The potential benefits of the 3DP4ME model may include the ability for each audiologist to treat more patients, and speeding access to custom devices at the same time.
Toward a Pilot Program
The pilot program launched in November is helping children with hearing loss in Jordan. Half will be Jordianian natives, and the other half will be refugee children from Palestine, Syria and Iraq currently living in camps in Jordan. The pilot will provide 50 children, ages 6-10, with subsidized hearing aids that include custom earmolds made from silicone (this softer material is more forgiving and better suited to kids’ ears than acrylic). Today a hearing aid in Jordan costs about $1,000 (compare that to the average cost of $5,500 in the U.S.), and 3DP4ME aims to offer these devices for around $500 with the help of funding from donors and sponsors.
Kids will be prescreened, then see an audiologist for a full diagnostic validation. Family will be interviewed at the 3DP4ME office to learn how each child's quality of life has been affected by hearing loss, and then the patient’s ears will be scanned. The nonprofit’s goal is that every child selected for this program will have a fitting with their custom hearing aids within two weeks. Follow-up speech therapy will also be provided for each patient.
Once this pilot is complete, 3DP4ME will open its services to all ages and start to offer acrylic earmolds as well as silicone. The organization recently signed an agreement with the Noor Al Hussein Foundation’s Institute for Family Health (IFH), which provides healthcare services throughout Jordan. IFH audiologists will help with the earmold pilot program and support future efforts by 3DP4ME, expanding the organization’s reach.
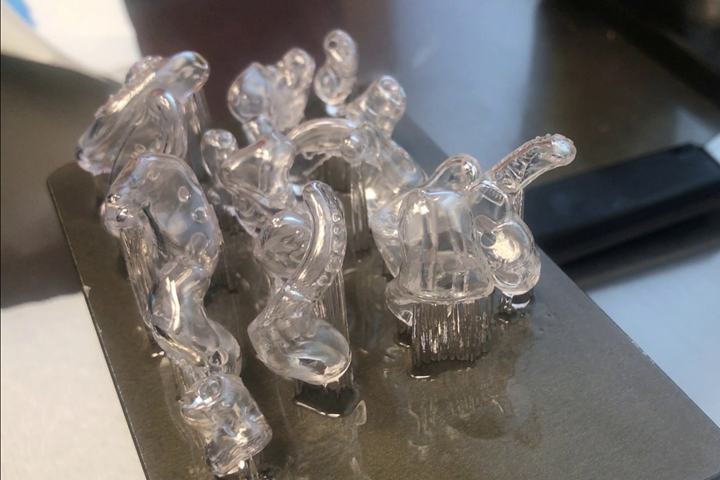

3DP4ME will print thousands of earmolds like this over the next few years as the organization grows its reach. Photo Credit: Microsonic Inc.
Once the process has been proven in Jordan, Szolomayer has his sights set on neighboring Syria. One in four people in the country has at least one disability, he says, and hearing loss is prevalent because of bombings and other acts of war. A mobile version of hearing treatment could be part of this future, in which the nonprofit could send a mobile van to remote locations to scan patients and then deliver completed devices.
But hearing aids are also not the only devices the organization aims to produce. 3DP4ME is also exploring partnerships to provide lower limb prosthetics for patients in these two countries. The process for creating these prosthetics would look similar to the hearing aid pilot program, with patients coming to the organization's office for scans and fittings, but with production outsourced to an EOS facility in Germany. The idea is still in progress, but it will be a step toward the ultimate goal:
"We want to be a full additive manufacturing facility for multiple assistive technologies," Szolomayer says.
Related Content
Durable, Waterproof 3D Printed Casts: The Cool Parts Show #58
Recovering from an injury with an ActivArmor cast means that patients can exercise, bathe and live life while they heal. We get a firsthand look at the solution in this episode of The Cool Parts Show.
Read More8 Cool Parts From Formnext 2023: The Cool Parts Show #65
New additive manufacturing technologies on display at Formnext were in many cases producing notable end-use components. Here are some of the coolest parts we found at this year’s show.
Read More3D Printing as a New Product Launchpad
With 3D printing, Minnesota manufacturer Resolution Medical offers a fast, affordable route for individuals and small to medium-sized businesses to get new medical devices and other products off the ground and into the marketplace.
Read MoreFrom Polymer Tooling to Metal Production Via 3D Printing
As Azoth has adopted new additive manufacturing technologies, its work has transitioned from tooling to production parts for automotive, medical and defense.
Read MoreRead Next
Fitz Frames Brings Mass Customization to Eyewear with Affordable 3D Printed Glasses Frames
Glasses don’t need to be ill-fitting and frustrating to buy. Fitz Frames offers a different kind of shopping experience (using augmented reality and 3D measurement) to produce custom glasses with 3D printed frames that are affordable, durable, comfortable and stylish.
Read More3D Printing Is the Next Step for Digital Dentistry
Digital dentistry is a workflow rather than a single technology. A conversation with Rik Jacobs of 3D Systems explores how 3D printing is participating in and advancing this workflow.
Read MoreMachine Learning for Invention Will Aid and Be Aided By AM
Neural networks that learn by trial and error—learning, in fact, like a child—will map the constraints of AM systems, allowing part designs to be optimized for those systems.
Read More

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)


















