3D Printing Method for Complex Metal-Plastic Composite Structures
Researchers from Japan and Singapore have developed a new 3D printing technique to create precise patterns on the external and internal surfaces of 3D plastic structures.
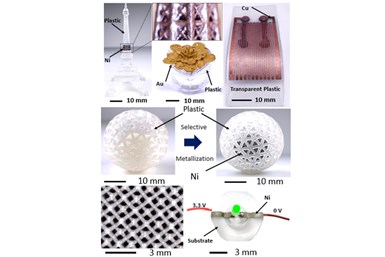
Examples of 3D metal-plastic composites that can be prepared by the new technology. Photo Credit: Professor Shinjiro Umezu from Waseda University
In recent years, research interest in the 3D printing of metal patterns on plastic parts has grown exponentially, due to its high potential in the manufacturing of next-generation electronics. But fabricating such complex parts through conventional means is not easy. Now, researchers from Japan and Singapore have developed a new 3D printing process for the fabrication of 3D metal-plastic composite structures with complex shapes.
Three-dimensional (3D) metal-plastic composite structures have widespread potential applicability in smart electronics, micro/nanosensing, internet-of-things (IoT) devices and even quantum computing. Devices constructed using these structures have a higher degree of design freedom, and can have more complex features, complex geometry and increasingly smaller sizes. But current methods to fabricate such parts are expensive and complicated.
Recently, a group of researchers from Japan and Singapore developed a new multimaterial digital light processing 3D printing (MM-DLP3DP) process to fabricate metal-plastic composite structures with arbitrarily complex shapes.
Robots and IoT devices are evolving at a lightning pace. Thus, the technology to manufacture them must evolve as well, according to the study’s lead authors Professor Shinjiro Umezu and Kewei Song from Waseda University, and Professor Hirotaka Sato from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Although existing technology can manufacture 3D circuits, stacking flat circuits is still an active area of research. The researchers wanted to address this issue to create highly functional devices to promote the progress and development of human society. The study has been published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
The MM-DLP3DP process is a multistep process that begins with the preparation of the active precursors — chemicals which can be converted into the desired chemical after 3D printing, as the desired chemical cannot be 3D printed itself. Here, palladium ions are added to light-cured resins to prepare the active precursors. This is done to promote electroless plating (ELP), a process that describes the auto-catalytic reduction of metal ions in an aqueous solution to form a metal coating. Next, the MM-DL3DP apparatus is used to fabricate microstructures containing nested regions of the resin or the active precursor. Finally, these materials are directly plated, and 3D metal patterns are added to them using ELP.
The research team manufactured a variety of parts with complex topologies to demonstrate the manufacturing capabilities of the proposed technique. These parts had complex structures with multimaterial nesting layers, including microporous and tiny hollow structures, the smallest of which was 40 micron in size. Moreover, the metal patterns on these parts were very specific and could be precisely controlled. The team also manufactured 3D circuit boards with complex metal topologies, like an LED stereo circuit with nickel and a double-sided 3D circuit with copper.
According to the researchers, using the MM-DLP3DP process, arbitrarily complex metal-plastic 3D parts having specific metal patterns can be fabricated. Furthermore, selectively inducing metal deposition using active precursors can provide higher quality metal coatings. Together, these factors can contribute to the development of highly integrated and customizable 3D microelectronics.
Researchers say the new manufacturing process promises to be a breakthrough technology for the manufacturing of circuits with applications in a diverse variety of technologies, including 3D electronics, metamaterials, flexible wearable devices and metal hollow electrodes.
- Listen to this AM Radio podcast with Stephanie Hendrixson and Products Finishing’s Scott Francis who discuss how conventional finishing techniques like electroplating and powder coating have a role to play in additive manufacturing.
Related Content
Drones Take Flight with Metal and Polymer 3D Printed Parts: The Cool Parts Show Bonus
Drones produced by Cobra Aero now incorporate many 3D printed parts made through laser powder bed fusion and Multi Jet Fusion processes.
Read More8 Cool Parts From RAPID+TCT 2022: The Cool Parts Show #46
AM parts for applications from automotive to aircraft to furniture, in materials including ceramic, foam, metal and copper-coated polymer.
Read MoreHow Large-Format 3D Printing Supports Micro-Scale Hydropower
There is potential hydroelectric power that has never been unlocked because of the difficulty in capturing it. At Cadens, additive manufacturing is the key to customizing micro-scale water turbine systems to generate electricity from smaller dams and waterways.
Read MoreHow to Improve Polymer AM Productivity 20X
A fast cycle time is critical to efficient production 3D printing, but it’s not the only thing. How you choose the right parts for AM, prepare jobs for production, and manage post processing will have just as big an impact on total 3D printing throughput. It all needs to work together to achieve maximum productivity.
Read MoreRead Next
3D Printing Brings Sustainability, Accessibility to Glass Manufacturing
Australian startup Maple Glass Printing has developed a process for extruding glass into artwork, lab implements and architectural elements. Along the way, the company has also found more efficient ways of recycling this material.
Read MoreHybrid Additive Manufacturing Machine Tools Continue to Make Gains (Includes Video)
The hybrid machine tool is an idea that continues to advance. Two important developments of recent years expand the possibilities for this platform.
Read More4 Ways the Education and Training Challenge Is Different for Additive Manufacturing
The advance of additive manufacturing means we need more professionals educated in AM technology.
Read More













.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)