10 Years Producing Hip Implants Through AM
There is already heritage in additive manufacturing. AM is taken seriously today in part because early users such as Lima Corporate have proven it.
Share
Read Next
When it comes to production parts made through AM, the success of the application often is not as well established as the appearance of the part would suggest. Making a part through 3D printing is one thing. Achieving a process that will produce that part to demanding specifications and do so consistently is more challenging. The difference accounts for why usable 3D-printed parts are common, while established 3D-printing production processes are less so.
But there is a flip side to this. Those production AM processes that are established frequently have been established for longer than one might expect. The reason why AM seemed to catch on several years ago as a viable and promising production option is because manufacturers in various sectors had been working for years earlier to develop and prove out industrial applications of what would come to be called AM.
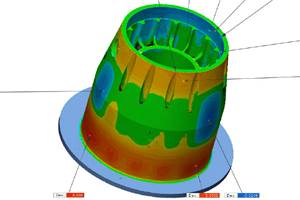
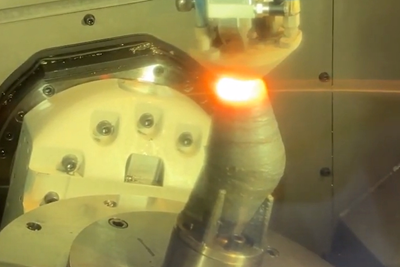
This year, one example of that pioneering work arrives at a milestone. It was 10 years ago that Italian medical device manufacturer Lima Corporate brought to market its first hip implant component produced through additive manufacturing. Additive allows the titanium cup of a hip implant to be made with precise surface geometry carefully engineered to encourage the growth of the patient’s bone into this surface. The specific process the company uses to make implants in this way is electron beam melting (EBM) on machines from Arcam. The company now manufactures various joint replacement implant components on 15 EBM machines. And in the time since it began, various other medical manufacturers have advanced with their own 3D-printed implant products. Indeed, Arcam president and CEO Magnus René says AM for medical implants is farther along than most manufacturers realize.
“People have two misconceptions about implants produced additively,” he says. “First, they think additive is solely for custom implants. It’s not.” In the medical industry, mass production of implant cups is far and away the most widespread use of EBM. “Second, people think additively produced implants are not approved by regulators.” Not only are AM implants approved for patients in Lima’s European market, he says, they are also approved in Japan, Australia, China and by the United States’ FDA.
Yet adoption has advanced only gradually, for various reasons he cites. The medical industry is understandably risk-averse, while insurance companies are not just risk-averse but cost-averse as well. Metal AM remains a relatively expensive process. Meanwhile, one other factor he sees helps account for why the Italian company was an early success. In the United States, hip implants are produced by a few large companies that would have to invest significantly to embrace a new manufacturing approach. In Europe, by contrast, hip implants are made by smaller companies that can change more nimbly. (He observes that spine implants in the United States are made by companies that are smaller, and these have moved into 3D printing more quickly.)
The use of AM for medical implants will continue to advance, he says. He sees this in the investments medical manufacturers are making in additive equipment, and the plans they are making for future products produced through AM. Plus, while additive technology steadily improves and can be expected to get less expensive, traditional implant manufacturing processes will continue to have their traditional drawbacks. Namely, these processes need dedicated tooling for steps such as forging, and they entail a range of operations from forging through various machining steps through plasma spray. AM can replace this with a tooling-free process consisting of just 3D printing and light machining.
Given all of this, the full adoption of AM for implant production is not a bold expectation in his view, but a reasonable inference from current trends.
“In five to 10 years,” he says, “I expect that all implants will be made additively.”
Related Content
Aalberts Surface Technologies Forms U.S. Heat Treatment Business Unit
Combining 17 diverse facilities into Aalberts Surface Technologies - HIP|Braze|Heat Treatment makes it one of the largest providers of thermal processing and metal joining technologies in the U.S.
Read MoreHow Does Heat Treating Affect Machining Considerations for a Metal 3D Printed Part?
This picture of part distortion in additive manufacturing illustrates the kind of effects that part design or machining stock allowances need to anticipate.
Read MoreAM 101: What Is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)? (Includes Video)
Hot isostatic pressing has long been used for metal castings, but is now being applied as a valuable method for closing porosity in metal 3D printed parts.
Read MoreElementum 3D’s High-Strength Aluminum Alloy Eliminates Need for Heat Treatment
Elementum 3D’s A5083-RAM5 aluminum alloy enables manufacturers to print advanced components from a high-strength aluminum alloy with reduced postprocessing time and cost.
Read MoreRead Next
Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Machine Tools Continue to Make Gains (Includes Video)
The hybrid machine tool is an idea that continues to advance. Two important developments of recent years expand the possibilities for this platform.
Read More3D Printing Brings Sustainability, Accessibility to Glass Manufacturing
Australian startup Maple Glass Printing has developed a process for extruding glass into artwork, lab implements and architectural elements. Along the way, the company has also found more efficient ways of recycling this material.
Read MoreAt General Atomics, Do Unmanned Aerial Systems Reveal the Future of Aircraft Manufacturing?
The maker of the Predator and SkyGuardian remote aircraft can implement additive manufacturing more rapidly and widely than the makers of other types of planes. The role of 3D printing in current and future UAS components hints at how far AM can go to save cost and time in aircraft production and design.
Read More