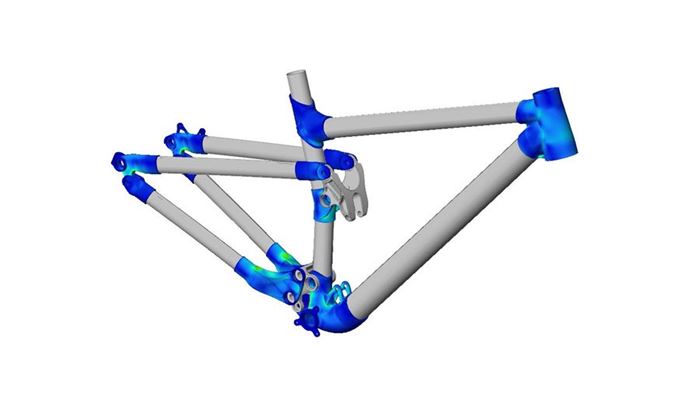
Customizable Bike Frame Developed with Additive Manufacturing
A bike frame featuring metal 3D-printed components demonstrates the potential for mass customization.
It doesn’t matter how good a bike frame is if it doesn’t fit the rider. This is where Robot Bike Co. (RBC), based in the United Kingdom, sees the weakness in the current market offerings.
“If you are trying to produce the very best frame it makes no sense to then only offer it in a small number of sizes when the people you are selling it to come in all shapes and sizes,” says RBC’s Ed Haythornthwaite. Haythornthwaite is one of four founders of RBC, the others being Ben Farmer, Andy Hawkins and Ben Robarts-Arnold. Since 2013, the company has designed and produced custom mountain bike frames.
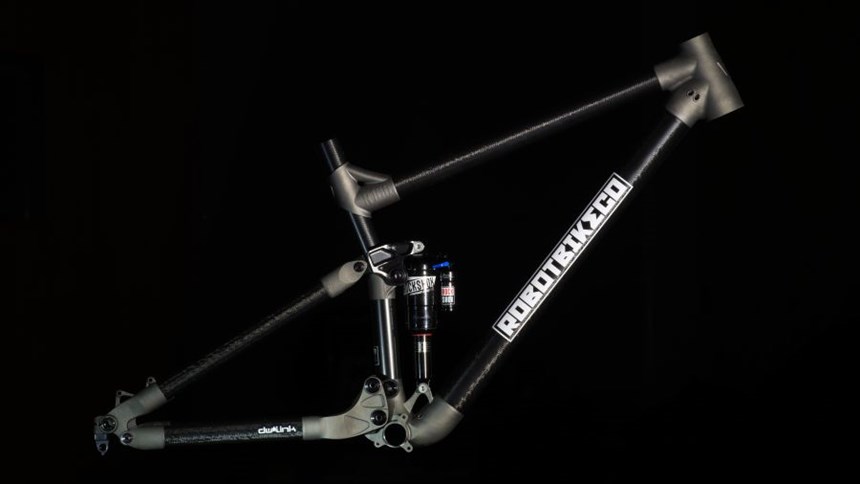
RBC recently unveiled its R160 mountain bike frame, designed and manufactured in the United Kingdom with the help of partner companies Altair, HiETA Technologies and Renishaw using metal additive manufacturing. Using a combination of selective laser melting, machining and carbon composite components, the project demonstrates how mass customization of bike frames could be possible.
AM development and project engineering specialist HiETA covers product design, manufacturing readiness and project management service from conceptual design to early-stage manufacturing. The company helped lead the project and shepherd it through to completion.
RBC designed the mountain bike frame concept, working with Dave Weagle, a well-known suspension designer, to develop and tailor the suspension design. The frame architecture places high strength-to-weight ratio titanium in high stress areas through 3D-printed joints, and connects them with carbon composite tubes which provide a high stiffness-to-weight ratio.
Simulation specialist Altair was responsible for optimizing the bike’s additively manufactured connecters. Using SolidThinking Inspire software, Altair was able to identify where material in the lugs could be removed to save weight and reduce part count without compromising performance.
“Additive manufacturing is the perfect partner for design optimization techniques as it allows us to produce components and systems that are far closer to the ideal balance of weight and performance,” says Paul Kirkham, team leader at Altair’s Bristol office.
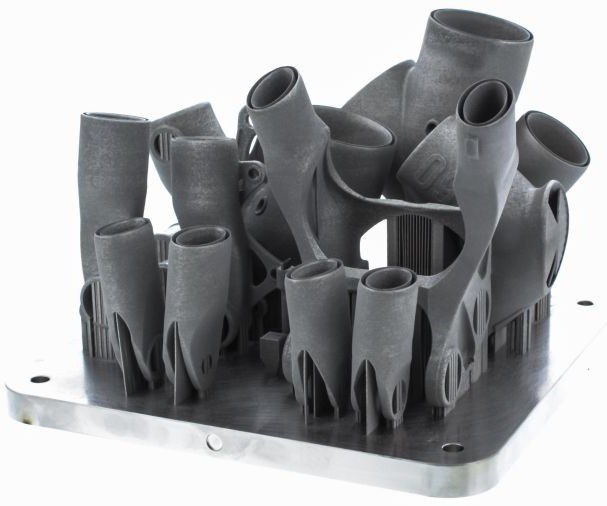
Renishaw lent its expertise in additive manufacturing, machining and metrology to the project. Renishaw is the UK’s only manufacturer of metal additive manufacturing systems, and its RenAM 500M selective laser melting machine was used to manufacture the lugs of the bike frame from aerospace-grade Ti6Al4V. Following printing, the lugs were heat-treated and CNC machined.
RBC says that every lug can be made to order to suit bike riders. And because the production process is not constrained by a mold, the frame can be tailored to customers’ individual measurements or specifications and can be constantly improved as new technologies emerge.
“One of the great aspirations of additive manufacturing has always been mass customization,” says Mike Adams, CEO of HiETA. “Leading this project has allowed us to see integration of all the elements—a great new frame design, the use of state-of-the-art software tools for optimization and automation, the flexibility of the manufacturing process itself and effective collaboration between our partners is a great advert for the technologies and the South West of England showcasing that the aspiration is becoming a reality.”
The bike frame will retail for around 4,395 pounds (about $5,838 at the time of posting) with a lead time of four weeks.
Related Content
NMPA Certifies Farsoon 3D Printed Tantalum Interspinal Fusion Cage
The company says the additively manufactured implants can be fully customized according to patients’ conditions, and the trabecular microstructure can achieve a high porosity of 68-78% to promote bone tissue and vessel fusion.
Read More3D Printed Lattices Replace Foam for Customized Helmet Padding: The Cool Parts Show #62
“Digital materials” resulting from engineered flexible polymer structures made through additive manufacturing are tunable to the application and can be tailored to the head of the wearer.
Read More8 Cool Parts From Formnext 2023: The Cool Parts Show #65
New additive manufacturing technologies on display at Formnext were in many cases producing notable end-use components. Here are some of the coolest parts we found at this year’s show.
Read More3D Systems’ VSP Bolus Optimizes Radiotherapy Targeting
The system is designed to enable the creation of a more personalized bolus made from a soft material that contours to the patient’s anatomy, enabling a more efficacious treatment and a more comfortable experience.
Read MoreRead Next
4 Ways the Education and Training Challenge Is Different for Additive Manufacturing
The advance of additive manufacturing means we need more professionals educated in AM technology.
Read More3D Printing Brings Sustainability, Accessibility to Glass Manufacturing
Australian startup Maple Glass Printing has developed a process for extruding glass into artwork, lab implements and architectural elements. Along the way, the company has also found more efficient ways of recycling this material.
Read MoreAt General Atomics, Do Unmanned Aerial Systems Reveal the Future of Aircraft Manufacturing?
The maker of the Predator and SkyGuardian remote aircraft can implement additive manufacturing more rapidly and widely than the makers of other types of planes. The role of 3D printing in current and future UAS components hints at how far AM can go to save cost and time in aircraft production and design.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)